Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide. It’s characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in specific areas known as tender points. These points can be extremely sensitive to touch, causing significant pain and discomfort. Managing this pain is a crucial aspect of living with fibromyalgia. This comprehensive guide provides practical strategies and insights to help you cope with fibromyalgia tender point pain effectively.
Understanding Fibromyalgia Tender Points
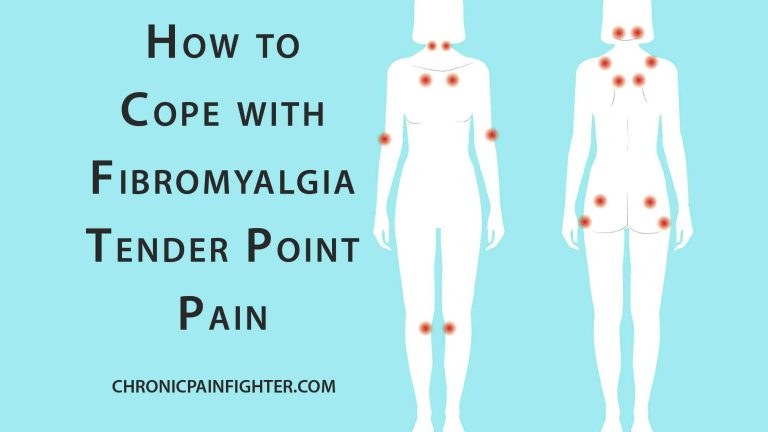
Fibromyalgia tender points are located in specific areas of the body, typically on both sides. These points are particularly sensitive to pressure, causing intense pain even with a light touch. While the exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, research suggests that the condition may involve dysfunction in the way the brain processes pain signals.
Here are some of the common fibromyalgia tender point locations:
- Occipital: At the base of the skull
- Trapezius: Between the neck and shoulder
- Supraspinatus: Top of the shoulder blade
- Second rib: Second rib just below the collarbone
- Lateral epicondyle: Outer elbow
- Gluteal: Buttocks
- Greater trochanter: Hip bone
- Knee: Just below the kneecap
Strategies for Coping with Tender Point Pain
Managing fibromyalgia tender point pain requires a multifaceted approach that combines various strategies tailored to your individual needs.
1. Pain Management Techniques:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and pain. However, long-term use of NSAIDs may have side effects, so consult with your doctor before taking them regularly.
- Prescription Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medications specifically for fibromyalgia pain, such as antidepressants (like duloxetine or milnacipran) or anticonvulsants (like pregabalin or gabapentin). These medications help regulate nerve signals and reduce pain perception.
- Topical Analgesics: Creams, gels, or patches containing capsaicin or lidocaine can provide localized pain relief by numbing the skin and blocking pain signals.
2. Physical Therapies:
- Gentle Exercise: Regular physical activity, like walking, swimming, or yoga, can improve muscle strength, flexibility, and overall fitness. Avoid high-impact exercises that might exacerbate pain.
- Massage Therapy: Massage can help relieve muscle tension and improve blood flow, promoting relaxation and pain reduction.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises and stretches specifically designed to strengthen muscles, improve range of motion, and reduce pain.
3. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Stress Management: Stress can worsen fibromyalgia pain. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to manage stress levels.
- Adequate Sleep: Sleep deprivation can exacerbate pain and fatigue. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can support overall health and potentially reduce inflammation.
- Heat Therapy: Applying heat to tender points using a heating pad or warm bath can soothe muscles and reduce pain.
- Cold Therapy: Using an ice pack wrapped in a towel on tender points can help numb pain and reduce inflammation.
4. Complementary Therapies:
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and reduce pain.
- Tai Chi and Qigong: These mind-body practices combine gentle movements with deep breathing to improve flexibility, balance, and pain management.
5. Support and Coping Mechanisms:
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have fibromyalgia can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help you challenge negative thoughts and beliefs related to pain and develop coping strategies to manage pain effectively.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: These practices can help you become more aware of your body, reduce stress, and promote relaxation.
6. Working with Your Healthcare Provider
It’s crucial to work closely with your doctor to develop an individualized pain management plan that suits your needs.
Here are some tips for communicating with your healthcare provider:
- Keep a pain diary to track your symptoms, including the intensity, location, and duration of pain.
- Share your concerns and questions openly with your doctor.
- Be honest about your medications and therapies, including over-the-counter remedies and supplements.
- Actively participate in your treatment decisions and ask questions about potential side effects and benefits.
Conclusion
Living with fibromyalgia tender point pain can be challenging, but it’s important to remember that you are not alone. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage your pain and improve your quality of life. Remember that pain management is a continuous process, and finding the right combination of strategies may take time and experimentation. Stay patient, stay informed, and seek support when needed.