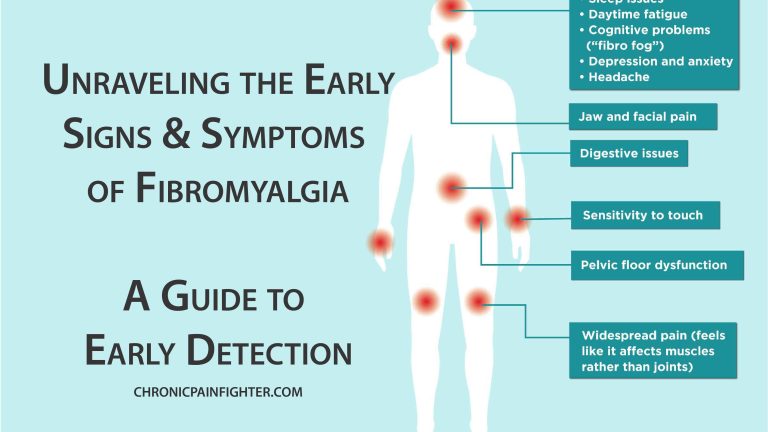
Fibromyalgia, a chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness, affects millions worldwide. The elusive nature of the disease, with its varied and often overlapping symptoms, makes early diagnosis challenging. However, understanding the subtle early signs and symptoms can pave the way for timely intervention and improved management of this condition.
This article delves into the early manifestations of fibromyalgia, aiming to empower individuals to recognize the potential warning signs and seek appropriate medical evaluation.
The Enigma of Fibromyalgia: Unveiling the Early Clues
Fibromyalgia’s initial stages often present a complex tapestry of symptoms, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact cause. The pain associated with fibromyalgia is often described as a deep, aching, and persistent discomfort that extends throughout the body, rather than localized to a specific area. This pain can be exacerbated by physical activity, stress, and even changes in weather.
Common Early Signs and Symptoms:
1. Widespread Pain: Fibromyalgia’s defining characteristic is the presence of widespread musculoskeletal pain, affecting both sides of the body and extending to areas above and below the waist. While pain in the neck, shoulders, back, hips, and legs is common, it can also involve the arms, hands, feet, and even the face.
2. Tender Points: Another hallmark of fibromyalgia is the presence of tender points, specific areas on the body that are hypersensitive to pressure. When pressed lightly, these points elicit pain that is more intense than what would be expected in someone without fibromyalgia.
3. Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is another prominent symptom, often described as overwhelming and persistent, even after adequate sleep. This fatigue can interfere with daily activities and make even simple tasks feel exhausting.
4. Sleep Disturbances: Poor sleep quality is a common companion to fibromyalgia, with individuals struggling to fall asleep, stay asleep, or experience unrefreshing sleep. This sleep disruption further contributes to the debilitating fatigue associated with the condition.
5. Cognitive Difficulties: Fibromyalgia can also impact cognitive function, known as “fibro fog.” This may manifest as difficulty concentrating, remembering things, or making decisions. This cognitive impairment can make it challenging to manage daily tasks and responsibilities.
6. Mood Changes: Fibromyalgia is often linked to mood changes, including increased anxiety, depression, and irritability. The chronic pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances can contribute to emotional distress and negatively impact mental well-being.
7. Other Symptoms: While not universally experienced, other symptoms may accompany the core symptoms of fibromyalgia. These may include:
- Headaches: Frequent or chronic headaches can be a symptom.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Digestive issues, such as abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits, are commonly reported.
- Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS): An urge to move the legs, often accompanied by unpleasant sensations, can also be present.
The Importance of Early Recognition:
Early recognition of fibromyalgia symptoms is crucial for several reasons:
- Prompt Medical Evaluation: Early diagnosis allows individuals to begin appropriate treatment, manage symptoms, and improve their overall quality of life.
- Effective Treatment Options: The earlier fibromyalgia is diagnosed, the more likely it is that treatment options will be effective in controlling symptoms and preventing further complications.
- Avoiding Misdiagnosis: Recognizing early signs and symptoms can help prevent misdiagnosis and unnecessary testing, saving time, resources, and emotional distress.
Navigating the Path to Diagnosis: A Collaborative Approach
If you suspect you may be experiencing early signs of fibromyalgia, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can perform a comprehensive evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history review, and potentially laboratory tests to rule out other conditions.
Diagnostic Tools:
There is no single definitive test for fibromyalgia. Diagnosis is often based on a combination of factors, including:
- Clinical Assessment: A thorough medical history and physical examination, with specific attention to the presence of widespread pain, tender points, and other associated symptoms.
- Symptom Severity: Assessing the intensity, frequency, and duration of symptoms, as well as their impact on daily life.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: Ruling out other medical conditions that could mimic fibromyalgia symptoms, such as arthritis, thyroid disorders, or infections.
The Role of Collaboration:
While a physician plays a critical role in diagnosing fibromyalgia, the process of early detection often involves collaboration between the patient and their healthcare provider. Open communication, accurate self-reporting of symptoms, and proactive involvement in the diagnostic process are essential.
Empowering Individuals: Taking Charge of Your Health
Early recognition and diagnosis are critical steps in managing fibromyalgia. Once diagnosed, a comprehensive treatment plan can be tailored to address the individual’s specific needs.
Treatment Strategies:
Treatment for fibromyalgia typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, encompassing:
- Pharmacological Therapy: Pain medications, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants are often used to manage pain, improve sleep, and reduce mood changes.
- Non-Pharmacological Therapies: Non-drug interventions, such as exercise, physical therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and relaxation techniques, play a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making adjustments to lifestyle factors, such as sleep hygiene, stress management, and dietary changes, can contribute to better symptom control.
A Journey of Hope: Living Well with Fibromyalgia
Living with fibromyalgia can be challenging, but with proper care and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. The key is to seek early diagnosis, engage in active management of symptoms, and build a supportive network of healthcare professionals and loved ones. By understanding the early signs and symptoms of fibromyalgia, individuals can take proactive steps to enhance their health and well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- Early detection of fibromyalgia is crucial for effective symptom management and improved quality of life.
- Recognize the common early signs, such as widespread pain, tender points, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties.
- Seek prompt medical evaluation if you suspect you may have fibromyalgia.
- Collaborate with your healthcare provider to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Embrace a holistic approach to managing fibromyalgia, incorporating pharmacological therapies, non-pharmacological interventions, and lifestyle modifications.
By empowering individuals to understand the early signs and symptoms of fibromyalgia, we can contribute to earlier diagnosis, improved treatment outcomes, and a brighter future for those living with this complex condition.